Big data is a phrase which is used to describe a very large amount of structured (or unstructured) data. This data is so “big” that it gets problematic to be handled using conventional database techniques and software. A Big Data Scientist is a business employee who is responsible for handling and statistically evaluating large amounts of data. The most important task of a Big Data Scientist is to describe the significance of bulk data in a way which could be easily understood.
 The term “Big data” sometimes can also be used to describe the tools and procedures an organization might need to process a large volume of data. Since the studies reflect that around 91% of the data today has been created in the last 3 years, the need for data handling has led to a need of developing and using Big Data Technologies.
The term “Big data” sometimes can also be used to describe the tools and procedures an organization might need to process a large volume of data. Since the studies reflect that around 91% of the data today has been created in the last 3 years, the need for data handling has led to a need of developing and using Big Data Technologies.
Clear examples of Big Data could be:
- Around 600 million tweets are sent in a day. This is more than 6,840 tweets per second.
- VISA handles around 172,800,000 card transactions every day.
The 3 Vs in Big Data
Big data is generally explained by using the 3 Vs which are: Variety, Velocity and Volume.
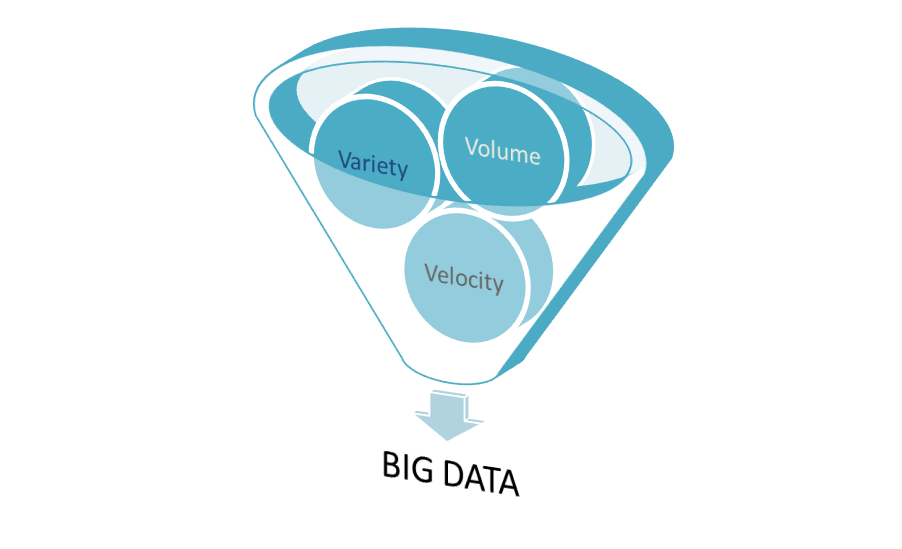 Variety refers to the largely varying formats of data, like databases, excel sheets, documents and several other commonly existing formats.
Variety refers to the largely varying formats of data, like databases, excel sheets, documents and several other commonly existing formats.
Velocity refers to the rate which with the data keeps changing, or in other words the rate at which data is created and updated.
Volume refers to the size of the available data. Today, data size has become enormous, ranging from giga bytes to even peta bytes.
Major Big Data Technologies
Several technologies and frameworks have been deveoped to handle big data. Some of the most popualar big data technologies are:
- Hadoop (or Apache Hadoop)– This is by far the most popular Big Data tool. It has an open source platform with a framework which is very flexible to handle multiple data sources. It can be used for ensuring maintenance, error-handling and security of Big data. One of the major applications of Hadoop is to process and manage large volumes of persistantly changing data.
- Map Reduce– This is a foundation framework for Hadoop. It allows handling of massive volumes of data in parallely distributed processing environment.
- No Sql– These are referred to as Not only Sql databases, which are very different from the traditional “relational” databases. Unlike the relational databases, nosql do not require any specific table schemas for data handling.
- Grid Computing – This is a special type of distributed computing where a connection is established between multiple geographically dispersed computer sources. These resources operate in parallel to handle large chunks of data.
- In-memory databases – These are databases which use the main memory of the system for data processing. These are used in systems where response time and data requests are considerably high.
- Specialized databases – These are big databases which manage and process data providing specific information.
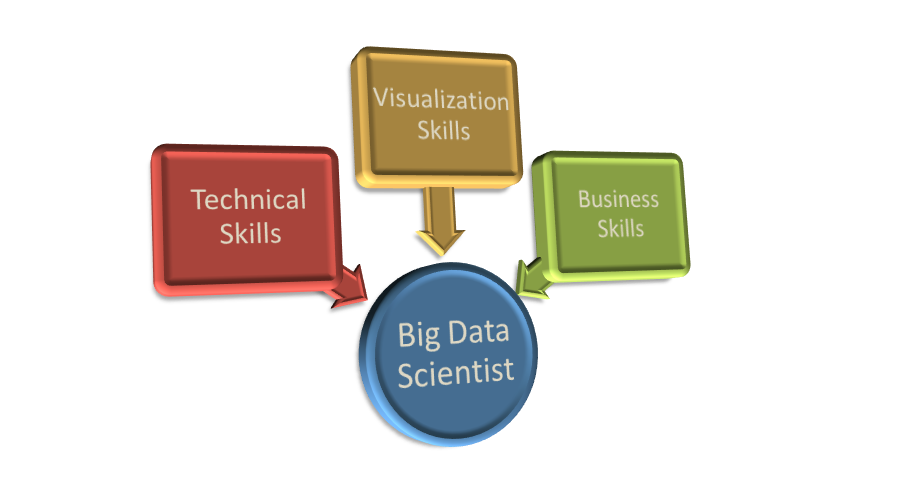
Skills Required to Become a Big Data Scientist
A Data Scientist must have a set of technical skills, visualization skills and business domain expertise. A data scientist should also posses strong analytical and problem solving skills.
- Knowledge of atleast one big data technology such as Hadoop.
- Knowledge of programming and scripting languages like Java and Python.
- Knowledge of database managament and SQL.
- Knowledge of data modelling and relational databases.
- Knowledge of statistical tools like SAS and Excel.
2. Visualization Skills: These include presentation skills and knowedge of tools like Powerpoint, Google Visualization API, Tableau, MS Paint etc.
3. Business Skills: These include knowledge of the business domain where you’re going to work, understanding and meeting the business needs, knowledge of risk analysis etc.
Big Data Applications
Big data has a number of applications for the capital market companies:
- Exploring data – Finding and managing the useful data is a big challenge for every enterprise. Big Data technologies can help these enterprises in exploring the “big” data.
- Risk Analytics – Risks, frauds and security could be controlled by using big data technologies. This could benefit in banking, insurance etc.
- Trading Analytics – Companies can analyse their customer base and their needs by using big data technlogies for data processing.
- Medical Data Management – Big data can help in managing the patient data in the medical sector.
- Telecom Data Management – Big data can be used to decrease the processing time by managing the call data in telecom sector. This could also optimize the locations based telecom services.
- Financial data management – Financial services companies process a several millions of transactions everyday. Big data technologies can help such companies in managing such a massively big data.
- Tax Compliance – Big data could help in detecting tax related frauds.
- Data tagging – Big data can help in organizing information by associating pieces of data with
Career Prospects
India is human capital rich country. The introduction of new technologies and the constantly increasing data has created a great need for professionals skilled in managing this “big” data.
There are various roles which could be played by a big data professionals:
- Big Data Scientist
- Big Data Analyst
- Big Data Visualizer
- Big Data Manager
- Big Data Solutions Architect
- Big Data Engineer
- Big Data Researcher
- Big Data Consultant
Firms like EMC, ORACLE , IBM and CAPGEMINI are planning to hire Big Data Scientists in the upcoming future.
Find Big Data Courses and Trainers Today!








Pingback: Software Engineering as a Career | ThinkVidya.com
Pingback: Some Popular IT Courses in Current Market | ThinkVidya.com
Pingback: Learn Hadoop and Big Data | ThinkVidya.com
Pingback: Why Should you Become a Data Scientist | ThinkVidya.com